Principle of peptide bond formation in custom synthesis of peptides
On the surface, the formation of peptide bonds (producing dipeptides) is a simple chemical process. This means that the two amino acid components are joined by a peptide bond (amide bond) and dehydrated at the same time.
Peptide bond formation is the activation of an amino acid under mild reaction conditions. (A) the carboxyl part, A second amino acid (B), and then the nucleophilically activated carboxyl part forms a dipeptide (A-B). If the carboxyl component (A) is not protected, peptide bond formation cannot be controlled. By-products such as linear peptides and cyclic peptides may mix with the target compound A-B. Therefore, all functional groups that are not involved in peptide bond formation during peptide synthesis must be protected in a temporarily reversible manner.The following is how peptide bonds are formed during custom peptide synthesis.
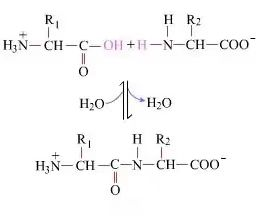
Therefore, peptide synthesis - that is, the formation of each peptide bond - consists of three steps of aggregation.
The first step: is to prepare some amino acids that need to be protected, and the zwitterionic structure of amino acids no longer exists;
The second step: is a two-step reaction to form peptide bonds, in which the carboxyl group of the N-protecting amino acid is first activated as an active intermediate and then forms peptide bonds. This coupling reaction can be either a one-step reaction or two continuous reactions.
The third step is to selectively remove or completely remove the protective group. Although all removal can only be done after all peptide chains have been assembled, selective removal of protective groups is also required in order to continue peptide synthesis.
Peptide synthesis is further complicated because 10 amino acids (Ser, Thr, Tyr, Asp, Glu, Lys, Arg, His, Sec, and Cys) contain side chain functional groups that require selective protection. A distinction must be made between temporary and semi-permanent protection bases because of different requirements for selectivity. Temporary protection groups are used to reflect the temporary protection of amino acids or carboxyl functional groups in the next step. Semi-permanent protective groups are removed without interfering with formed peptide bonds or amino acid side chains, sometimes during synthesis.
Ideally, the activation of carboxyl components and the subsequent formation of peptide bonds (coupling reactions) should be a rapid reaction, with no racemization or by-products formed, and molar reactants applied to obtain high yields. Unfortunately, no chemical coupling method can meet these requirements, and few are suitable for actual synthesis.
During peptide synthesis, functional groups involved in various reactions are often attached to manual centers (glycine is the only exception), and there is a potential risk of rotation.
The final step in the peptide synthesis cycle is to remove all protective groups. Selective removal of protective groups is important for peptide chain extension in addition to the complete removal of protective groups in dipeptide synthesis. The synthesis strategy should be carefully planned. Depending on the strategic choice, N can selectively remove α-amino protective groups or carboxyl protective groups. The term "strategy" refers to the sequence of condensation reactions of individual amino acids. In general, there is a difference between progressive synthesis and fragment condensation. Peptide synthesis (also known as "conventional synthesis") takes place in solution. In most cases, the gradual elongation of the peptide chain can only be synthesized by synthesizing shorter fragments using the peptide chain. In order to synthesize longer peptides, the target molecules must be segmented into suitable fragments and determined that they can minimize the degree of differentiation at the C-end. After the individual fragments are gradually assembled, the target compound will be connected. The strategy of peptide synthesis includes the selection of the best and most suitable protective fragments, and the strategy of peptide synthesis includes the selection of the most appropriate protective group combination and the best fragment coupling method.
Read Related Articles:
Copyright © 2020 Omizzur Inc | Terms & Conditions | Privacy Notice | Sitemap