TFA Removal From Peptides
In peptide synthesis, most peptides are isolated and purified under the TFA system, so peptides are most in the form of TFA salts, followed by drug peptides are generally in the form of acetate and hydrochloride, very few drug peptides will have some special salt forms, under normal circumstances, peptides are customized in the form of TFA delivery, its content may be between 10%-40%.
Tfa Structural Formula:
In the process of solid-phase synthesis of peptides, trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) is often used to cut peptides from solid-phase resins. Trifluoroacetic acid or acetic acid are also used in the process of purifying peptides by reverse phase HPLC. But if used as a peptide in preclinical and clinical studies, residual trifluoroacetic acid or fluoride will be toxic and unpopular.
TFA may bring many problems. Therefore, we can remove TFA salts and avoid them from the beginning. TFA is a strong acid, so it can protonate any amino group. The same goes for hydrochloric acid. One technique used in reverse phase HPLC during the purification of peptides is anion exchange.
The peptides synthesized by the company are generally in the form of TFA salts. If residual TFA will affect your experiment, we usually recommend converting it to other salts, such as acetic acid and hydrochloride forms. These salt forms of peptides typically cost 20% to 30% more than TFA salts, due to the loss of some peptides during salt conversion and the need for more raw materials. TFA removal from peptides can be necessary.
Types of Peptide Salts in Peptide Synthesis:
1. Trifluoroacetate (TFA): This is a salt commonly used in peptide products, but due to the biological toxicity of TFA, some experiments need to avoid using this salt. For example, cell experiments.
2. Acetate (AC): The biological toxicity of acetic acid is much lower than that of trifluoroacetic acid, so most pharmaceutical and cosmetic peptides use acetate. However, some products have unstable acetate, so sequence stability also needs to be considered. Most cell experiments choose to use acetate.
3. Hydrochloride (HCL): This salt is rarely selected, and only some sequences use hydrochloride for special purposes.
4. Ammonium salt (NH4+): This salt can seriously affect the solubility and stability of the product and must be selected in order.
5. Sodium salt (NA+): Generally, it can also affect the stability, solubility, etc. of the product.
6. Palmicacid: This salt is often used in peptide drugs to make sustained-release agents.
7. Citric Acid: This salt has relatively low physiological toxicity, but the preparation process is very complex, so the production process needs to be developed separately in sequence.
8. Salicylicacid: Salicylates can affect the stability of peptide products and are therefore rarely used.
| Type | Applications |
| TFA | It is a residual salt from the process of chemical synthesis of peptides and has certain cytotoxicity |
| AC | Acetate is less cytotoxic than TFA, but the stability of the polypeptide in acetic acid also needs to be considered |
| HCL | Hydrochloride is usually used for special purposes |
| NH4+ | This kind of salt will seriously affect the solubility and stability of the product, and must be selected according to the sequence |
| Pamoic acid | It is often used in peptide drugs to make sustained-release agents |
The above are several types of peptide salts, and we also need to choose according to the characteristics of different salts in actual use.

Load the peptide onto the column, keep it at the top, wash with sufficient acetic acid buffer, and then perform gradient elution with acetic acid aqueous solution/acetonitrile. After freeze-drying, the counter ion TFA is exchanged. This technology relies on the hydrophobicity of peptides. A peptide with high hydrophilicity will require a suitable anion exchange resin.
How to choose the correct peptide salt? Does TFA only regulate PH in the buffer? The higher the concentration of TFA, the greater the baseline drift. Does that mean that the concentration of TFA is as low as the buffer PH allows?
(1) TFA plays a similar role to ion pairs, the general concentration is 0.05-0.1%, too high concentration, will make the solution acidic, long-term use may affect the life of the column.
(2) At the same time, TFA can inhibit the silanol group on the surface of silica gel and improve the peak type of alkaline compounds. Sometimes 0.1%TFA separation is not good. Consider increasing the concentration to 0.2%. But pay attention to rinse the column in time after use.
(3) When the gradient is taken, the baseline drift is caused by the walk, but it has little effect on the preparation.
TFA is a strong acid. It can protonate any amino group. The same goes for hydrochloric acid. In the process of purification of peptides by reverse-phase HPLC, one technique is anion exchange. Load the polypeptide onto the column, keeping it on top, while washing with sufficient acetic acid buffer, then gradient elution with acetic acid aqueous solution/acetonitrile.
After freeze-drying, the counterion TFA is exchanged. The technique relies on the hydrophobicity of the peptides. A high hydrophilic polypeptide will require a suitable anion exchange resin. The use of a special reversed-phase C-18 material provides a good separation method to remove TFA.
About Omizzur Biotech
Omizzur Bio can provide customized peptide synthesis TFA remove or conversion services.These salt forms of peptides are typically 20% to 30% more expensive than TFA salts, due to the loss of part of the peptide and the need for more raw materials in the salt transfer process, which is mostly ion exchange and HPLC methods, while desalination can be done with dialysis bags and ultrafiltration membranes. For informations about custom peptide synthesis companies pls visit Omizzur homepage.
FAQs:
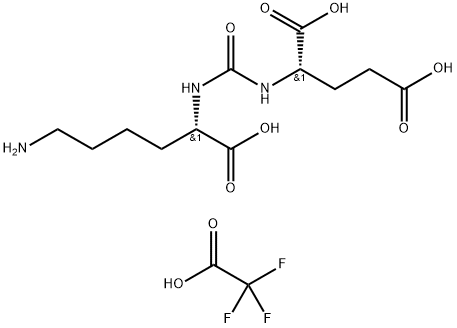
What is TFA Salt?
| Name | TFA / Trifluoroacetate |
| Alias | (2S)-2-(3-((S)-5-amino-1-carboxypentyl)ureido)pentanedioic acid TFA |
| CAS | 1269794-89-9 |
| Molecular formula | C14H22F3N3O9 |
| Molecular weight | 433.34 |
| Solubility | Water : 160 mg/mL (369.23 mM; Need ultrasonic) |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
Copyright © 2020 Omizzur Inc | Terms & Conditions | Privacy Notice | Sitemap