Study on impurities in salmon calcitonin (1)
The European Pharmacopoeia API contains 4 known impurities, namely N-acetylcysteine salmon calcitonin, 9-D leucine salmon calcitonin, des-22-tyrosine salmon calcitonin, and O-acetylsalmon calcitonin; There are two main impurities in domestic raw materials, one is N-acetylcysteine salmon calcitonin, and the other is an unknown impurity with a RRt of 0.9; However, there are mainly two unknown impurities in the raw material, with RRt of 0.9 and 0.73, respectively. It is inferred that these two impurities are process impurities generated during solid phase synthesis.
In the solid phase synthesis process of salmon calcitonin, theoretically possible impurities include the following categories:
Amino acid deficient salmon calcitonin impurity. Salmon calcitonin lacks a peptide impurity of one amino acid, and there are 32 possible impurities ranging from the deletion of N-terminal cysteine to the C-terminal proline. For example, the impurity Cnor-22 tyrosine Salmon calcitonin in the European Pharmacopoeia 7.0 is analyzed from its amino acid properties, and acidic amino acids such as aspartic acid and glutamic acid are not easy to condense. Salmon calcitonin is a peptide impurity that lacks two amino acids and may have more types, such as C-terminal glycine threonine deficient Salmon calcitonin
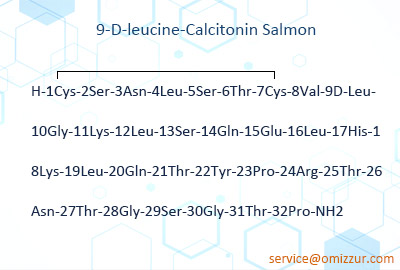
Chiral racemic isomers are produced due to the chiral racemization of certain amino acids such as cysteine, serine, lysine, histidine, proline, and arginine during the condensation process during solid-state synthesis. The latter is a missing peptide lacking asparagine in the peptide chain, which may be produced due to the influence of amide bonds in asparagine during condensation, making the amino acid difficult to condense. As impurity B, 9-D leucine salmon calcitonin in European Pharmacopoeia 7.0
Degradation impurities, such as hydrolytic impurities, some amino acids are relatively easy to hydrolyze, such as asparagine, glutamine, and the amide structure formed by terminal proline is also easy to hydrolyze; Oxidizing impurities, impurities that are oxidized by cysteine, such as impurity D in European Pharmacopoeia 7.0; Amino acid ring opening impurity, proline ring opening, two proline in salmon calcitonin, easy to open the ring to form 5-aminovaleric acid; N-terminal acetylated impurity, such as impurity A in European Pharmacopoeia 7.0
Proline ring opening impurity
[H-Cys-Ser-Asn-Leu-Ser-Thr-Cys]-Val-Leu-Gly-Lys-Leu-Ser-Gln-Glu-Leu-His-Lys-Leu-Gln-Thr-Tyr-Ava-Arg-Thr-Asn-Thr-Gly-Ser-Gly-Thr-Pro-NH 2
Recombinant salmon calcitonin impurity
Salmon calcitonin impurities from recombinant sources are given in European Pharmacopoeia 7.0
Impurity E Calcitonin salmon-glycine:
C[H-Cys-Ser-Asn-Leu-Ser-Thr-Cys]-Val-Leu-Gly-Lys-Leu-Ser-Gln-Glu-Leu-His-Lys-Leu-Gln-Thr-Tyr-Pro-Arg-Thr-Asn-Thr-Gly-Ser-Gly-Thr-Pro-NH-CH2-CO2H
Impurity F 1,7-bis (3-sulfo-l-alanine)] calcitonin (salmon)
Impurity G 1,7-bis (3-sulfo-l-alanine)] calcitoninylglycine (salmon)
---
Article from Omizzur: custom peptide impurity synthesis India
Copyright © 2020 Omizzur Inc | Terms & Conditions | Privacy Notice | Sitemap