Polypeptide modification:PEGylation
Omizzur provides customized pegylated conjugations, peptides and small molecules pegylated and custom peptides synthesis services.
Pegylation refers to the linking of polyethylene glycol (PEG) to a polypeptide through covalent bonds. The molecular weight of proteins and peptides increased after pegylation and were not hydrolyzed by protease, and the pharmacokinetics were improved.Pegylation also reduces renal clearance, allowing for sustained absorption despite subcutaneous administration and limited dispersion. Pegylation has been shown to significantly improve water solubility, biocompatibility, immunogenicity and other physicochemical properties, and is a mature method for biological drug delivery.
Glutathione (GSH) is a tripeptide composed of glutamic acid, cysteine and glycine that is active in many biological REDOX reactions. The binding of glutathione to its pegylated liposome across the blood-brain barrier through sodium-dependent transport can enhance the delivery of fluorescent labels in the brain.
Pharmacological advantage of pegylation of polypeptides
1:Improve the solubility of polypeptides and protect them from protein degradation. PEG polymers, and their associated water molecules, provide protection against enzymatic degradation of the linked polypeptide drug, thus limiting adverse immune responses. Pegylated peptides are more stable over a range of pH and temperature variations than unpegylated peptides.
2:Reduce the frequency of administration and reduce potential toxicity. PEG is less toxic and can be completely cleared from the body by kidney (pegylated drugs <30 kDa) or stool (pegylated drugs >20 kDa).
3:Increase the stability of peptides or drugs, prolong the cycle life. PEG lacks immunogenicity, and only by binding to high immunogenicity proteins can anti-PEG antibodies be produced in rabbits.
PEG-modified
1: PEG-maleimide, molecular weight 1K, 2K, 5K, 10K, 20K, or 30K
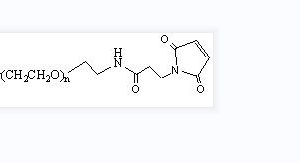
2: Maleimide -PEG- Maleimide, molecular weight 1K, 2K, 5K, 10K, 20K, or 30K
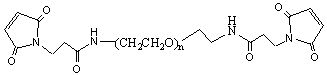
3: Mini-PEG:AEEA, 9 Carbons, CAS number: 166108-71-0; 2-[2-[2-(Fmoc-amino)ethoxy]ethoxy]acetic acid; Molecular weight: 385.42 g/mol; C21H23NO6
4:Mini-PEG2, AEEP, CAS number: 872679-70-4; Fmoc-NH-PEG2-Propionic Acid; 9-(Fmoc-amino)-4,7-dioxanonanoic acid; Molecular weight: 399.5 g/mol; C22H25NO6
5:Mini-PEG3, Fmoc-AEEEA, CAS number: 139338-72-0; Fmoc-NH-(PEG)3-COOH, or 2-[2-[2-[2-(Fmoc-amino)ethoxy]ethoxy]ethoxy]acetic acid; Molecular weight: 429.47 g/mol; C23H27NO7
6:Mini-PEG4, Fmoc-AEEEEP, CAS number: 557756-85-1; Fmoc-NH-PEG4-Propionic Acid, or Fmoc-15-amino-4,7,10,13-tetraoxapentadecacanoic acid; Molecular weight: 487.6 g/mol; C26H33NO8
7:Mini-PEG5, Fmoc-AEEEEEP, CAS number: 882847-32-7; Fmoc-NH-PEG5-Propionic acid, or Fmoc-18-amino-4,7,10,13,16-pentaoxaoctadecanoic acid; Molecular weight: 531.6 g/mol; C28H37NO9
Read Related Articles:
Copyright © 2020 Omizzur Inc | Terms & Conditions | Privacy Notice | Sitemap