Aggregation forms and classification of Aβ oligomers
Introduction:Amyloid plaques (also known as age spots) appear outside AD brain nerve cells and on cerebrovascular walls, and it is believed that this kind of amyloid plaques may be an important cause of AD
Abstract: AD is one of the most common forms of Alzheimer's disease. Although people still lack A clear understanding of the etiology of AD, it is generally believed that Aβ is A very important protein related to the pathogenesis of AD. This protein has an obvious feature that it is easy to self-aggregation, so the aggregation form and process of Aβ are considered to be highly relevant to the etiology of AD.Aβ mainly exists in monomer, oligomer and fiber in vivo and in vitro, among which Aβ oligomer is considered to be an important cause of AD pathogenesis, and the studies related to Aβ oligomer are increasing. In this paper, the toxicity, molecular structure, classification and significance of Aβ oligomer are analyzed and summarized.
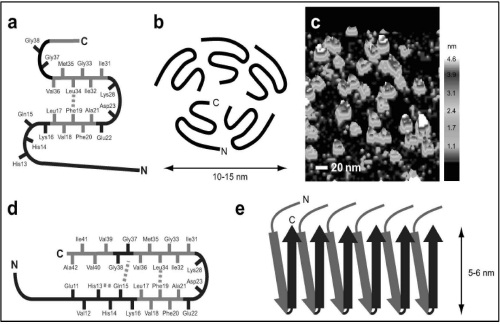
1. Aβ soluble oligomer is considered to be the main cause of AD
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of senile dementia. Clinically, the pathological symptoms of AD patients mainly include: Neuronal decay, amyloid plaques appear outside the nerve cells of the brain and cerebrovascular walls, and a large number of neuronal fiber disorder (NFT) appear in the neuron cells, and the survival time of about 7 years after the disease. According to a 2007 report in nature, there are currently 4.5 million AD patients in the United States alone, and the number of AD patients around the world is increasing. Therefore, it is very urgent to understand the etiology of AD as soon as possible and carry out effective treatment in clinic.
Amyloid plaques (also known as senile plaques) appear outside AD brain nerve cells and on cerebrovascular walls. It is believed that this amyloid plaques are likely to be an important cause of AD. In the 1980s, the main protein components in plaques were extracted and purified. This protein is called beta-amyloid protein (Aβ). It is A 39-43 amino acid fragment of the single transmembrane protein APP that is formed by β-secretase and γ-secretase.
One of the most important features of Aβ protein is that it is very easy to aggregate, so the protein mainly exists in the form of monomer, oligomer and fiber. Until the mid to late 1990s, it was widely believed that Aβ fiber was the important cause of AD formation. As A result, the entire field of Aβ research has considered how to inhibit and reduce fiber may be an important approach to the treatment of AD. However, many researchers believe that the A-beta aggregates are the main cause of neuronal deterioration, and that the monomers are not toxic. However, under the conditions, oligomers and fibrous forms are not strictly distinguished.
2.Classification by molecular size is A common method for classification of Aβ oligomers
The question of whether some oligomers form fibers, which may be directly related to the physiological toxicity of some intermediate forms of fibers, continues to be debated, because the process of how Aβ monomers aggregate to form fibers is not well understood. Therefore, many people use TEM, AFM, west blot, SEC and other methods to study the process of protein formation. In addition, some studies compare the structure of Aβ with other amyloid proteins, such as HiApp, α-synuclein, amylin, etc. According to the morphology and classification of oligomers above, Several different views are generally held: Some fiber intermediates, such as Protofibrils and fibrils Genesis (including Protofibrils) are considered to be in a metastable state of fiber, and will certainly become fibrillary protein if prolonged incubation. However, there are some oligomerized forms of proteins that are considered to be the final form of Aβ aggregation, such as globulomer, Annular assemblies. But these issues are controversial
3.The names and characteristics of Aβ oligomers were classified by common methods
The classification of oligomers roughly has the following classification methods, according to molecular weight can be divided into low molecular weight oligomers and high molecular weight aggregates, according to the fiber form process can be divided into fiber intermediates, according to the shape can be divided into spherical oligomers and non-spherical oligomers
4. Difficulties to be overcome in oligomer classification
At present, the biggest problem in the study of AD is that it is difficult to obtain enough and pure Aβ oligomers in vivo. Although the synthetic Aβ oligomers also have specific toxicity and can replace the isolated proteins in vivo as research objects, However, the concentration of oligomers used in the study of the toxicity of these oligomers is much higher than that of the physiological and pathological Aβ oligomers. Some of them even use the concentration of about 10uM/ul in cell culture. In A work in nature, the natural soluble small molecule Aβ oligomers were isolated, and the concentration of which only needs the nanomolar level. This suggests that it will be challenging to find out which specific form or forms of natural Aβ oligomers play important toxic roles in AD for A long time to come.
Copyright © 2020 Omizzur Inc | Terms & Conditions | Privacy Notice | Sitemap